A Guide to AI Voice Cloners and Synthetic Speech
AI voice cloners are software tools that can listen to a person's speech and whip up a synthetic, digital copy of their voice. This isn't just a simple recording. The replica can be used to say things the original person never did, capturing their unique pitch, tone, and rhythm.
How Do AI Voice Cloners Actually Work?

Think of it like a master impressionist. They don't just mimic a famous person's voice; they study their laugh, their pauses, and the way they emphasize certain words. They get the essence of the person. AI voice cloning works in a similar way, breaking down a voice to its very core before it can build it back up. It's less about mimicry and more about a deep, digital understanding of what makes your voice yours.
This whole process is powered by some pretty sophisticated algorithms, specifically a type of AI called a neural network. These are complex systems designed to spot patterns in data, much like the human brain does. In this case, the data is your voice.
Getting from a short audio clip to a fully functional digital voice usually happens in three key stages. Each step builds on the one before it, sharpening the AI's understanding until it can create brand-new, convincing speech all on its own.
The Three Core Stages of Voice Cloning
First up is data collection. To learn your voice, the AI needs a sample. The cleaner the audio, the better the final result—that means no background noise, just clear speech. Years ago, you might have needed an hour of audio. Now, some of the best tools can get the job done with just a few minutes, or sometimes even seconds, of good-quality recording.
Next, we hit the training phase. This is where the magic really happens. The audio sample is fed into the neural network, which starts its analysis. It breaks the voice down into its most basic ingredients:
- Pitch: How high or low the voice is.
- Cadence: The natural rhythm and flow of speech.
- Timbre: The unique texture that makes a voice instantly recognizable.
- Intonation: The rise and fall in tone that injects emotion into words.
The AI isn’t just memorizing sounds. It's learning the rules of how a person speaks, creating a mathematical model—a sort of "vocal fingerprint."
This training phase is what separates simple playback from true synthesis. The AI is learning the underlying mechanics of a person's speech, which lets it predict how they would say words and phrases it has never encountered before.
Finally, we have the synthesis stage. Once the AI model is trained, it's ready to talk. You give it some text, and it uses that vocal fingerprint to build an audio waveform from scratch. It pieces together the basic units of sound (phonemes) and wraps them in all the unique vocal characteristics it learned.
The result is a synthetic voice that sounds remarkably like the real thing, ready for all sorts of applications. We're already seeing this tech being used in amazing ways, and you can get a glimpse of its potential in our guide on how to let AI handle your phone calls.
The Journey of Synthetic Voice Technology
To really get why modern AI voice cloners feel so magical, you have to look at where they came from. This whole quest to create synthetic speech didn't just pop up overnight. It’s a story that started decades before "AI" was a buzzword, back when machines could only produce clunky, robotic sounds that barely passed for human speech.
Watching the tech evolve from those monotone voices to the fluid, emotional speech we hear today has been an incredible ride. Early systems were rigid and rule-based, but they laid the groundwork for the powerful neural networks that are the engine behind today's most impressive voice cloning tools.
From Mechanical Speech to Digital Voices
The evolution of synthetic voice has been a long game, with roots stretching back to the 1960s. A huge moment came in 1968 when IBM showed off its Shoebox machine, an early device that could actually generate digitized speech from text. That breakthrough set the stage for the first commercial text-to-speech products in the 1980s, like DECtalk and MacinTalk, which brought synthetic voices into the mainstream for the first time.
The 1990s brought a major shift toward machine learning, which made synthetic speech sound way more natural. But the real explosion happened in 2016 when Google’s DeepMind created WaveNet, a model that could generate raw audio that was shockingly realistic. You can dive deeper into the history and learn more about its key milestones on Resemble.ai.
The Neural Network Revolution
The adoption of neural networks was the true turning point. Instead of just stitching together pre-recorded sound clips—a method known as concatenative synthesis—these new systems could actually learn the underlying patterns of human speech directly from audio.
This was a seismic shift. It meant AI models could now generate entirely new speech from the ground up, capturing all the subtle stuff—like pitch, cadence, and emotion—that makes a voice sound like a person.
The following screenshot gives you a peek under the hood, showing how a modern speech synthesis system turns text into sound.
This diagram shows just how much is going on, from analyzing the text to generating the final audio waveform, all to create a voice that's believable.
Deep learning models like WaveNet basically set a new gold standard for realism. For the first time, it was becoming tough to tell the difference between an AI voice and a real human recording. That’s what flung the doors wide open for the high-fidelity AI voice cloners we have today.
This breakthrough kicked progress into overdrive. What once took decades to inch forward could now be massively improved in just a couple of years, leading to the rapid-fire advancements we’re seeing in voice quality and cloning speed.
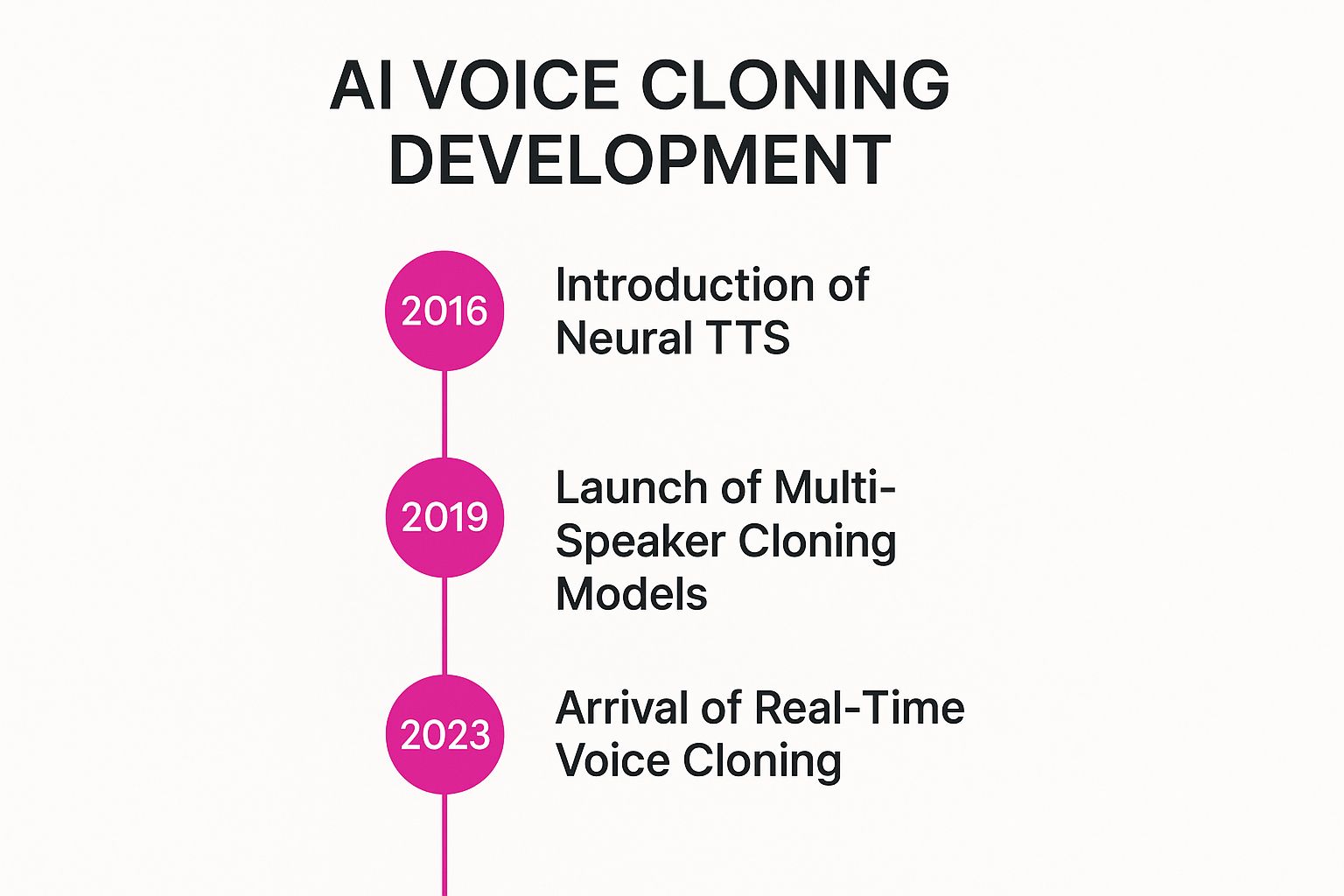
Key Milestones in Modern Voice Cloning
In the last few years, the pace has gone from fast to frantic. A few key moments have really defined the modern era of voice cloning.
This timeline visualizes three pivotal moments in the development of AI voice cloning technology.

The infographic perfectly captures how quickly we went from creating generic voices to cloning specific ones on the fly, all in less than a decade.
This incredible acceleration is thanks to three big developments:
- Neural Text-to-Speech (TTS): Around 2016, models started producing speech that was worlds away from the robotic tones of the past. It finally sounded natural.
- Multi-Speaker Models: By 2019, systems got smart enough to learn from tons of different speakers. This made it possible to clone a new voice from just a tiny audio sample.
- Real-Time Cloning: Since 2023, the tech has gotten so fast that it can clone and convert voices almost instantly. This was the final piece of the puzzle for live applications.
Understanding this history is key. Today's tools didn't just materialize out of thin air; they’re the result of a long, fascinating journey in our mission to give machines a human voice.
Real-World Applications of Voice Cloning

While the tech behind AI voice cloners is fascinating, the real magic happens when you see how it’s being used to solve actual problems and create entirely new possibilities. This isn't some far-off concept anymore; voice cloning is already making a real impact across industries, moving well beyond theory and into practical, everyday use.
From global entertainment to deeply personal accessibility tools, synthetic voice technology is opening doors that were previously shut tight. It's giving creators powerful new ways to tell stories and helping businesses connect with customers on a global scale.
The push for more realistic and emotionally expressive synthetic voices was kicked into high gear by the consumer tech market. It all started with early voice recognition features, like those Apple introduced way back in 2008, which laid the groundwork for assistants like Siri. This widespread adoption of voice interaction in our daily lives created a massive demand for better AI voices, fueling the development of the advanced AI voice cloners we see today. You can learn more about how consumer tech shaped AI voice trends on Canva.com.
Transforming Entertainment and Media
The entertainment industry was one of the first to jump on the voice cloning bandwagon, and for good reason. The technology offers clever solutions to old-school challenges in content creation, localization, and bringing characters to life, making media more immersive for everyone.
Take film dubbing, for instance. Traditionally, dubbing a movie meant hiring a new voice actor, which often meant losing the original performance's unique tone and emotion. With voice cloning, a director can now preserve the original actor's voice, translating their dialogue into different languages while keeping their distinct vocal identity. The result is a much more authentic viewing experience for audiences around the world.
Video games are another huge beneficiary. Developers can use a single actor's cloned voice to generate thousands of lines of dynamic dialogue for non-playable characters (NPCs). This saves a ton of studio time and allows for richer, more responsive game worlds where characters can react to player actions with unique, context-specific lines.
Revolutionizing Accessibility and Communication
Perhaps the most profound use of voice cloning lies in its power to restore a fundamental part of our identity: our voice. For people who have lost the ability to speak due to conditions like ALS or throat cancer, this technology is a lifeline.
Using past recordings, AI voice cloners can build a digital replica of a person's voice. This synthetic voice can then be hooked up to text-to-speech devices, allowing them to communicate with family and friends in a voice that is recognizably their own, not a generic, robotic one.
This process, often called "voice banking," is more than just a technological feat. It's a deeply human application that helps individuals preserve their identity and maintain personal connections in the face of life-altering health challenges.
Beyond personal restoration, voice cloning helps create more natural-sounding digital assistants and navigation tools, making technology more approachable for everyone. For businesses, this can mean creating personalized customer service experiences, like setting up unique and professional greetings for incoming calls. For more ideas on this, check out our guide with professional voicemail greeting examples.
Enhancing Business and Content Creation
For content creators and businesses, AI voice cloners are unlocking new levels of efficiency and personalization. The technology is being used in all sorts of ways to simplify workflows and create more engaging material.
- Podcasting and Audiobooks: Creators can now edit audio by simply editing a text transcript. If they misspeak or want to add a sentence, they just type the correction, and the AI generates the audio in their cloned voice. No more re-recording entire sections.
- Corporate Training: Companies can create consistent, high-quality training modules and update them on the fly without having to call back the original voice actor. This keeps all materials current and delivered in a familiar, professional voice.
- Personalized Advertising: Brands can generate thousands of ad variations tailored to different demographics. Imagine an ad that uses a cloned voice to mention specific locations or promotions—all without needing endless recording sessions.
AI Voice Cloning Applications Across Industries
Voice cloning isn't limited to just a few niche areas; its impact is spreading across a wide range of sectors. The table below highlights just a few key industries that are seeing significant benefits from this technology.
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Key Benefit | | --- | --- | --- | | Entertainment | Dubbing films and localizing game dialogue with original actor's voice. | Preserves artistic integrity and creates a more authentic global experience. | | Healthcare | Creating personalized synthetic voices for patients who have lost speech. | Restores personal identity and improves communication for patients. | | Marketing | Generating thousands of personalized ad variations for different audiences. | Achieves hyper-personalization at scale without massive recording costs. | | Education | Creating dynamic and easily updatable e-learning and training modules. | Increases efficiency and ensures content consistency and accessibility. | | Customer Service | Developing unique, branded voices for virtual assistants and IVR systems. | Enhances brand identity and provides a more natural customer experience. |
These examples make it clear that AI voice cloning is far more than a novelty. It's a practical tool that is already delivering serious value, changing how we create, communicate, and connect with one another.
Navigating the Ethical Maze of Voice Cloning
[Content type 'embed' not supported]
With any powerful tool, from the printing press to the internet, comes a serious sense of responsibility. AI voice cloners are no different. As this technology gets easier for anyone to use, it’s dragging a whole host of ethical questions out into the open. The ability to perfectly replicate a human voice opens the door to incredible creativity, but it also carries the potential for some serious harm if it falls into the wrong hands.
The heart of the problem is just how personal our voices are. A voice isn't just a bunch of sounds; it's a signature that signals trust, emotion, and authenticity. When that signature can be perfectly forged, it messes with our ability to believe what we hear, creating a whole new set of risks we need to figure out how to manage.
And this isn't some far-off, futuristic problem. We're already seeing reports of unauthorized voice cloning, where creators have found their voices being used in commercial videos without their permission. It’s a wakeup call that anyone with a public presence could have their vocal identity hijacked.
The Dangers of Misuse
The potential for AI voice cloners to be misused is huge, and frankly, a bit scary. Bad actors can use this tech to create incredibly convincing deepfake audio designed to trick and manipulate people. This can go wrong in a few key ways.
One of the biggest worries is fraud. Scammers can clone a voice to impersonate a loved one in a panic, creating a believable emergency call to trick someone into sending money. These scams hit us where we're most vulnerable—our instinct to help family—and they work because they sound so terrifyingly real. Learning how to stop robocalls is a good start, but deepfake audio adds a tough new layer to the fight.
The technology is also a major threat to public trust. Imagine political misinformation campaigns powered by fake audio clips of a candidate appearing to say something they never actually said. These kinds of deepfakes could be used to swing elections, cause chaos, and make people doubt everything they hear.
The unauthorized use of a person's voice for commercial gain is another major ethical breach. As seen in recent cases, companies could potentially clone a well-known personality's voice to endorse products, creating a false association that harms the individual's reputation and violates their right to control their own likeness.
The Path to Responsible Use
Facing these challenges doesn't mean we should just ditch the technology. Instead, it means we need to build a strong framework of safeguards and ethical rules to make sure it's used responsibly. This comes down to focusing on three critical areas.
First and foremost is the idea of unbreakable consent. It needs to be crystal clear that cloning a person's voice without their explicit, informed permission is completely unacceptable. This has to be the foundation of any ethical voice cloning platform, ensuring people always have the final say over their own vocal identity.
Second, we need to get better at spotting the fakes. A whole new field is popping up dedicated to creating smart algorithms that can detect the tiny, subtle clues in synthetic audio that the human ear might miss. This creates a much-needed reality check on the technology, making it way harder for bad actors to pass off deepfakes as the real thing.
Finally, we need clear legal rules. Lawmakers and tech companies have to work together to create laws that protect people from voice theft and fraudulent impersonation. There are already some legal precedents for protecting against vocal impersonation in ads, but we need new laws that specifically tackle the challenges posed by AI voice cloners.
By focusing on these proactive solutions, we can work to minimize the risks while still unlocking the incredible potential of voice cloning technology for good. It's a tricky balance that will require everyone—developers, users, and regulators—to stay on their toes.
The Future of Synthetic Voice and Market Trends

If you think today's AI voice cloners are impressive, just wait. We're standing at the foot of a massive technological wave, and the synthetic speech of today is just the beginning. The next generation of this tech isn't just about sounding more human—it's about capturing genuine emotional depth, working faster, and becoming accessible to everyone.
This isn't some niche hobby for tech enthusiasts; it's a full-blown market explosion. The demand for high-quality, believable voice AI is skyrocketing across almost every industry imaginable. It’s quickly becoming a fundamental tool for content creation, device interaction, and even how we communicate.
The numbers don't lie. The AI voice cloning market was valued at a cool USD 1.45 billion back in 2022. But it's not staying there. Projections show it rocketing forward with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.1% all the way through 2030. That kind of growth is fueled by real-world needs in entertainment, accessibility tools, and the ever-growing army of smart assistants. You can dig deeper into the future of AI voice cloning on Resemble.ai.
Emerging Trends in Voice Synthesis
The future is about making AI voices more dynamic, not just more realistic. A few key trends are pushing the boundaries of what AI voice cloners can do, and they're pretty exciting.
First up is real-time voice conversion. Picture this: you speak into your microphone, and your voice instantly transforms into another pre-selected voice on the other end. This is a game-changer for live streamers, gamers, and anyone in a virtual meeting who wants to present a different vocal persona on the fly.
Another huge leap is happening with singing voices. Early AI models sounded robotic and clunky when they tried to carry a tune. The latest systems, however, are learning to replicate the subtle vibrato, pitch shifts, and genuine emotion that make a singer's performance compelling.
Looking ahead, the focus will increasingly be on capturing the complete vocal identity. This means moving beyond simple mimicry to replicate laughter, sighs, and other non-speech sounds that make communication feel genuinely human and personal.
Finally, these tools are becoming incredibly easy to use. What once demanded a powerful computer and a degree in audio engineering is now being packed into simple, user-friendly apps. This is putting voice cloning into the hands of individual creators, small businesses, and artists, letting them experiment without breaking the bank.
The Market Outlook for AI Voice Technology
The money is following the innovation. The market for synthetic voice is buzzing with investment, which is pouring into research and development. This isn't just a fleeting trend; investors see AI voice cloners as a foundational technology for the next decade.
So, what's driving this massive expansion?
- Growing Content Demands: The world has an insatiable appetite for localized and personalized content. Voice cloning is the perfect tool for creating audiobooks, ads, and e-learning courses for different regions without hiring dozens of voice actors.
- Advancements in AI: Neural networks are getting smarter, faster, and cheaper to run. Every improvement makes the resulting voices sound even more realistic.
- Integration with IoT: Your smart speaker, your car, your fridge—they all need voices. As these devices get more common, the demand for natural, customizable voice assistants is only going to climb.
When you connect the dots between the tech breakthroughs and the market demand, the picture becomes crystal clear. Over the next few years, synthetic voices will be woven into the fabric of our digital lives, powering everything from our GPS directions to the virtual assistants that organize our day. The future isn't just about listening to AI—it's about giving it a voice that is convincingly, and uniquely, our own.
AI Voice Cloning: Your Questions Answered
As you start exploring synthetic speech, you’re bound to have questions. The idea of an AI voice cloner is fascinating, but it also brings up some practical and ethical points. We’ve rounded up the most common ones to give you clear, straight answers.